

About us Diamonds Contact Pricelist Guestbook Links
The famous 5 C's.
Diamonds are graded in the categories of color and
clarity. International grading scales have been developed
to ensure that diamonds across the world match in quality and value.
1) COLOR
White diamonds are valued for their lack of color.
The closer to color-free the stone, the more worth it has on the market.
Graduations of color in diamonds can be extremely subtle and are often
unnoticeable to the untrained and naked eye.
Diamonds categorized with the letters D, E, and F are considered to be
exceptional white gems, with letters G through H as white gems and
I through L signifying less valuable stones. Categories represented by letters M
through Z are considered to be “tinted” diamonds.
Colored diamonds are graded on the intensity of their color, as opposed to lack
of it. The most common colored diamonds are yellow,
brown (champagne and cognac), blue, green, and pink. Diamonds sold for their
color are labeled as “fancy” diamonds and some can
rival exceptional white diamonds in cost.

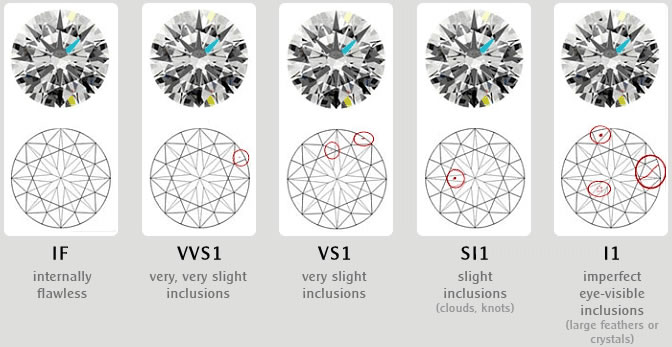
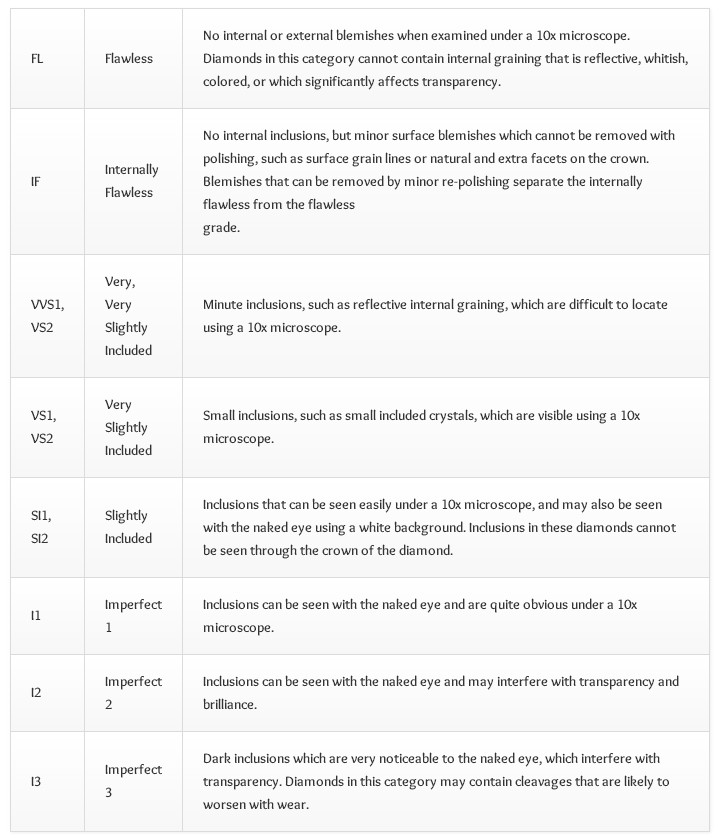
2) CLARITY
Imperfections within a diamond are call inclusions.
Inclusions are problematic because they interfere with
light’s ability to pass through the gem, which makes the diamond less brilliant
and therefore, less valuable.
The international scale for clarity rates diamonds on the number of inclusions
as well as the size and placement
of them in the diamond. Clarity ratings range from flawless, meaning there are
no inclusions present in the diamond,
to level 3 imperfect, which means dark inclusions can be seen with the naked
eye.
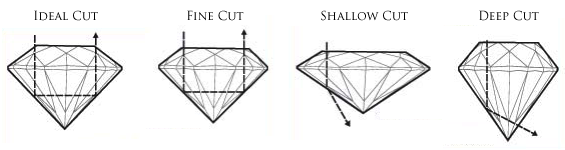
3) CUT
The traditional round, brilliant cut diamond
accounts for more than 75% of diamonds sold in today’s market.
A round shaped diamond offers the most options regarding the balancing cut,
color, and clarity of the gem, while
still getting the desired fire and brilliance. But cut means also the way how
the diamond is been cutted and the light reflection.
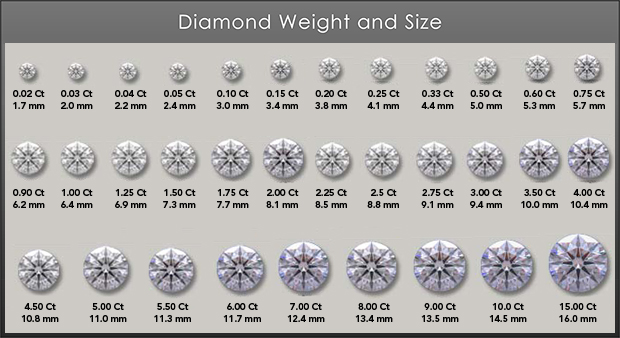
4) CARAT
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much
a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams.
Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This allows very precise
measurements to the hundredth decimal place.
A diamond dealer may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its
'points' alone. For instance, he may refer
to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a 'twenty-five pointer.' Diamond weights
greater than one carat are expressed
in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as 'one point zero
eight carats.
5) CONFIDENCE
Buying a diamond can be intimidating. Finding a
beautiful diamond is easy; finding the right one for your taste
and budget is more of a challenge. Unless you are a skilled gemologist, how can
you know, beyond a shadow of a doubt,
that the diamond you are considering is truly a quality one? After all, diamonds
are expensive. You want assurance
that the quality you’ve paid for is the quality you are getting.
The good news is that by following just one important step, you can have
complete peace of mind about your
diamond purchase. Always ask for an International certificate such as HRD, GIA
or IGI, with the
highest standards of diamond grading.
Daems Diamonds is only selling natural
certified diamonds, that have been purchased from legitimate sources
not involved in funding conflict and in compliance with United Nations
resolutions.

